News and Articles
Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) in logistics and transportation management

Autonomous Vehicles (AVs) are revolutionizing the logistics and transportation management industry by offering enhanced safety, efficiency, and sustainability. This technology is transforming the way goods are moved, from self-driving trucks and drones to autonomous ships, promising a future of more efficient and cost-effective transportation[1].
How Autonomous Vehicles Work
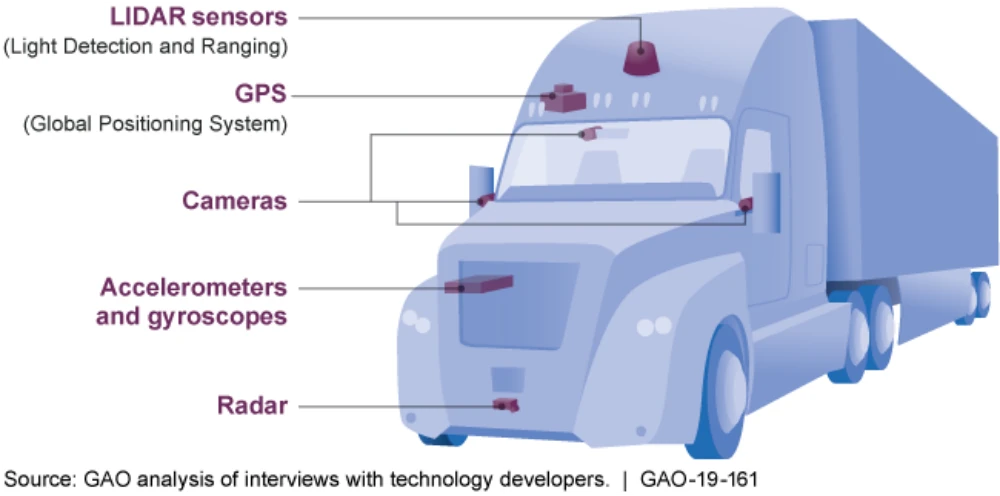
AVs are equipped with advanced technologies such as sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence, enabling them to perceive their surroundings, make real-time decisions, and navigate complex environments with precision. These vehicles can optimize routes, avoid collisions, and operate around the clock without breaks, significantly improving efficiency and reducing costs.
Benefits of Autonomous Vehicles
- Increased Safety: AVs can reduce accidents and fatalities on the road by eliminating human error, which is responsible for a significant number of road accidents.
- Reduced Costs: Autonomous vehicles can operate 24/7 without breaks, reducing the need for multiple drivers and improving efficiency.
- Improved Efficiency: AVs can optimize routes to avoid traffic and reduce delivery times. For last-mile deliveries, it can reduce the need for trucks to navigate congested urban areas.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Autonomous vehicles can optimize routes to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, as known as the carbon footprint of the industry.
Implementation Challenges and Constraints
- Regulatory Frameworks: There is a need for clear and comprehensive regulatory frameworks to ensure the safe integration of AVs onto public roads.
- Technological Limitations: While significant strides have been made, there are still limitations to overcome, especially in terms of ensuring reliable performance under diverse and unpredictable road condition.
- Public Acceptance: There are valid concerns about labor displacement within the driving profession, and public acceptance of AVs is still a challenge.
- Infrastructure: The development of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations and maintenance facilities, is crucial for the widespread adoption of AVs.
Case Studies in Thailand and Asia
- Thailand: The Thai government has launched initiatives to promote the use of electric vehicles (EVs) and AVs, with plans to have 50,000 EVs on the road by 2025. One example is Hutchison Ports Thailand (HPT) who has implemented the driverless electric trucks to improve safety and service levels at HPT’s Terminal D at Laem Chabang Port (more details: https://logistics-manager.com/th/hutchison-ports-thailand-are-driving-towards-the-future-with-autonomous-trucks/)
- Singapore: The city-state has been actively testing and implementing AVs, with companies like nuTonomy and ST Engineering conducting trials of self-driving taxis and buses.
- China: Companies like Baidu and Didi Chuxing are leading the development of AVs in China, with Baidu launching a self-driving taxi service in Beijing.
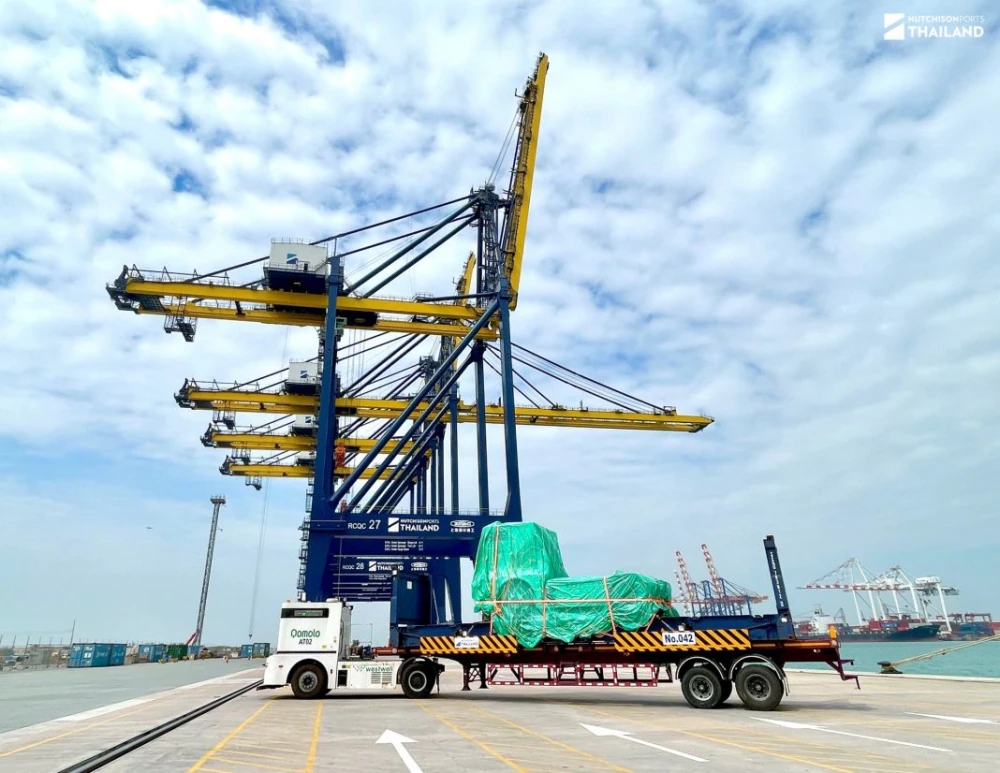

In conclusion, the future of autonomous vehicles in logistics and transportation management is promising, with significant benefits in safety, efficiency, and sustainability. While there are challenges to overcome, the potential for transformation is immense, and Asia is at the forefront of this revolution.
References:
- Hutchison Ports (Thailand) Limited. https://hutchisonports.co.th/hpt-9-at-eng/ and https://logistics-manager.com/th/hutchison-ports-thailand-are-driving-towards-the-future-with-autonomous-trucks/
- Kumar, A. (n.d.). Future of Autonomous Vehicles in Transportation and Logistics, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/future-autonomous-vehicles-transportation-logistics-ankit-kumar
- TCITransportation. (n.d.). The Future of Autonomous Vehicles in Freight Transportation, https://tcitransportation.com/blog/the-future-of-autonomous-vehicles-in-freight-transportation/
- Khan, M. (n.d.). Revolutionizing Logistics and Transportation: The Impact of Autonomous Vehicles, https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/revolutionizing-logistics-transportation-impact-vehicles-maaz-khan-
- ZhenHub. (n.d.). The Impact of Autonomous Vehicles in Logistics, https://zhenhub.com/blog/autonomous-vehicles/
- Singapore Government. (n.d.). Autonomous Vehicles, https://www.batonglobal.com/post/impact-of-autonomous-vehicles-in-your-supply-chain








